From the outside, it may seem that online payments are easy. You just need to attach your webpage to your chosen paying agent and you are ready to go. The money just flows.
I would really like it to be that simple. To be honest, sometimes things get a little more complicated. What acquiring means read on wellcoinpay.com right now. As in the verification process, when you set up your account to process payments, and after that, when you start accepting payments, you are likely to come across a certain vocabulary, terms that do not always seem obvious.
Fear not – in this post we have collected and summarized the most common definitions.
3-D Secure
Source: e-ghl.com
The authentication method developed by Visa is also used by other card organizations. The three-domain model (customer domain, issuer domain, and interaction domain) must have its own name.
3-D Secure makes the payment process safe and secure, protects against fraud, but can be a little inconvenient for some customers, as it adds another step (pop-up) to the transaction and may not handle mobile phones well.
Before you get involved, you need to think about the pros and cons (as well as additional fees).
Acquirer/acquirer bank
Trading bank. Its function is to connect the merchant, the card association, and the issuing bank (cardholder). The acquirer offers the merchant a line of credit (merchant account) and allows the merchant to accept payments by credit and debit cards.
The seller’s business is fraught with risk – it can be higher or lower, but it is always present. The acquiring bank shares the seller’s risks and additionally controls his operations. If there are too many questionable transactions, the bank may charge an additional commission.
Refundable payment

Source: northstarmeetingsgroup.com
A chargeback is, in its most concise definition, a refund of money paid. Chargeback protects customers, especially in cases of fraud and consumer disputes.
At the request of the cardholder and at the initiative of the issuing bank, the cardholder returns the funds to the client. However, unlike refunds, chargebacks are not convenient for merchants as they are subject to fines. If the percentage of chargebacks is too high, then the buyer will definitely rethink further cooperation with the seller.
Credit card
A plastic card that allows the owner to spend money on services and goods within the limit, which depends on the credit line provided by the issuer.
CVV / CVC

Source: nivoforlife.tv
Card security code generated by the card issuer. Improves the security of credit and debit card transactions.
Direct debit
This payment method works differently in different countries. In some processes, this happens automatically and is similar to paying by credit card, while in others it is done manually, and the merchant can only receive payment after the client’s written permission from his bank.
Fraud

Source: mumbaimirror.indiatimes.com
An unauthorized payment usually followed by a chargeback. A fraud risk assessment in a transaction can prevent many of these incidents.
High-Risk Trader
Some businesses are riskier than others. This could be due to a business model or product offering (such as travel services) that may be particularly prone to fall victim to chargebacks.
Acquiring banks classify risks and charge additional commissions to high-risk businesses.
Issuer/Issuing Bank

Source: chargebacks911.com
This is where the customer gets their credit card. A financial institution that may, but does not have to, be a bank connected to card networks (such as Visa, MasterCard, or American Express) and issue cards on their behalf.
Seller
A company that sells products online.
Merchant account

Source: facebookportraitproject.com
This is necessary if your business is sold online; one seller can have several such accounts.
A merchant account (line of credit) is created with an acquiring bank when the merchant enters into an agreement with the acquirer to process online payments.
The service is available for a fee and works in a similar way to a regular bank account, although, unlike a regular account, you cannot withdraw money “in the usual way”. Merchant accounts regularly transfer payments to others (corporate or private) accounts.
MO/payments
Order by mail or phone. A “no card” transaction, during which the buyer does not physically present the card to the merchant, but provides the required data by phone or email.
PCI DSS standards
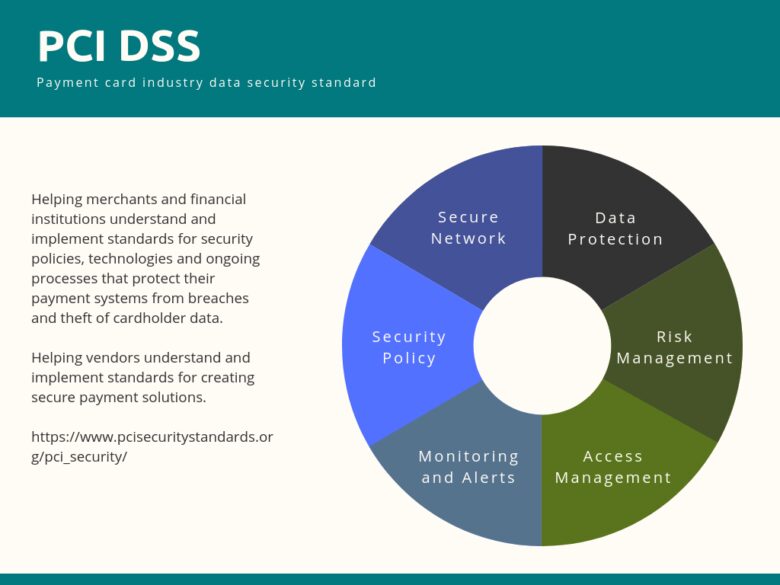
Source: avinetworks.com
Acronym for the payment card industry data security standards. If you are PCI compliant (and you should!), You become a more reliable seller.
Regular payment
Payment processing mechanism for recurring transactions. Also known as recurring invoices/subscriptions.
A certain amount of money is withdrawn from the card, the bank account, or PayPal at regular intervals (called a standing order and initiated by the payer), or variable amounts are charged by the merchant with the customer’s permission (direct debit).
Refund

Source: sellerengine.com
More welcome than chargebacks – the customer gets their money without bad consequences for the seller.
If a seller receives a complaint from a buyer, it is important to resolve the issue quickly and not leave any traces that could lead to a refund.
The right money back offer can really help your e-business grow.
Request to receive
Sometimes the card issuer asks the merchant for information about an e-commerce transaction.
The seller must respond to the request and provide the requested documentation. If the merchant does not do this, the request will automatically become a chargeback. After that, you will not be able to correct the situation if the refund was caused by the inability to respond to the refund request.
Mobile reserve

Source: gsiexchange.com
A buffer that allows the seller’s buyer to remain calm in the event of a sudden surge in chargebacks or a large number of chargebacks. A rolling reserve is used where there are risks, such as large average tickets, large processing volume, poor personal credit, etc.
It is usually created together with a trading account for a certain period of time and is based on the buyer’s deduction of a percentage of the transaction amount.
Settlement currency
The currency in which the merchant receives payments from their trading accounts.
Transaction currency

Source: lilliecpa.com
The currency in which the seller accepts payments for the product from buyers.
The transaction descriptor
This helps the buyer identify the transaction. A well-designed transaction descriptor will save you from embarrassing situations when a customer sends a chargeback just because they don’t recognize the purchase.
Depending on the merchant’s needs, they can use a static descriptor (one descriptor for all payments) or a dynamic descriptor for various services and products.
Cashless transfer
Electronic payment system. During the payment process, the buyer is redirected to the website of their bank, where they automatically approve the Bank transfer or enter the necessary data manually.
That’s it: the most used words in the world of online payments. Do you have anything to add? Let us know in the comments.




